
Beyond Chatbots: Exploring the Rise of AI Agents in Business
Introduction
The landscape of artificial intelligence is evolving at an unprecedented pace, constantly reshaping how businesses operate and interact with their customers. For years, chatbots have been the most visible manifestation of AI in customer service and basic automation, offering quick answers and streamlining simple tasks. However, the capabilities of AI have expanded far beyond these conversational interfaces. We are now witnessing the emergence of a more sophisticated form of artificial intelligence: AI agents. These intelligent entities are not merely programmed to follow a script; they possess the ability to reason, learn, and act autonomously to achieve complex goals. This paradigm shift from reactive chatbots to proactive AI agents marks a significant leap forward in business automation and strategic decision-making. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into what defines an AI agent, how they differ fundamentally from their chatbot predecessors, their diverse applications across various industries, the profound benefits they offer, and the challenges and considerations businesses must address as they embrace this transformative technology. Understanding this evolution is crucial for any organization looking to harness the full potential of AI for smarter business growth and sustained competitive advantage
AI agents are transforming various business functions, from operations to customer service.
What are AI Agents? Distinguishing Them from Chatbots
To truly appreciate the rise of AI agents, it’s essential to first understand their core characteristics and how they diverge from the more familiar chatbot technology. While both are designed to interact with users and automate tasks, their underlying architecture, capabilities, and operational scope are vastly different.
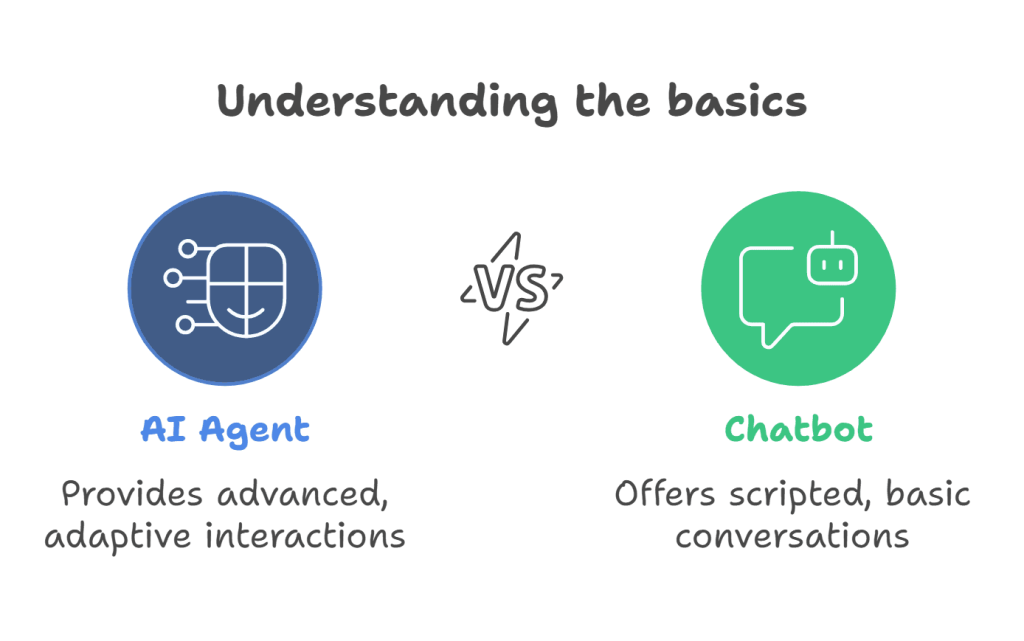
A visual representation highlighting the key differences between AI agents and traditional chatbots.
Chatbots: Rule-Based and Reactive
At their heart, traditional chatbots are typically rule-based or, in more advanced forms, rely on natural language processing (NLP) to understand user queries and provide pre-programmed responses. They are primarily reactive, meaning they wait for a user’s input before performing an action. Their functionality is often limited to specific, well-defined tasks, such as answering frequently asked questions, guiding users through a simple process, or providing basic information. Think of a chatbot as a highly efficient, automated FAQ system or a digital receptionist. They excel at handling high volumes of repetitive inquiries, reducing the workload on human agents, and providing instant support. However, their limitations become apparent when faced with complex, multi-step problems or situations that require reasoning, adaptation, or proactive engagement. They lack memory beyond the immediate conversation context and cannot initiate actions without explicit user prompts.
AI Agents: Autonomous, Proactive, and Goal-Oriented
In contrast, AI agents represent a significant evolution. An AI agent is an autonomous entity that perceives its environment, makes decisions, and takes actions to achieve a specific goal. Unlike chatbots, which are largely confined to conversational interfaces, AI agents can operate across various digital environments, including enterprise systems, databases, and even the internet. Their key distinguishing features include:
Autonomy: AI agents can operate independently, without constant human intervention. They can initiate actions based on their understanding of the environment and their assigned objectives.
Proactivity: Rather than merely reacting to user commands, AI agents can anticipate needs, identify opportunities, and take preemptive steps to achieve their goals. For example, an AI agent monitoring sales data might proactively suggest a marketing campaign based on emerging trends.
Goal-Oriented Behavior: AI agents are designed with specific, often complex, objectives in mind. They can break down a large goal into smaller sub-tasks, plan a sequence of actions, and execute them to reach the desired outcome. This involves a degree of reasoning and problem-solving capabilities.
Learning and Adaptation: Many AI agents incorporate machine learning algorithms, allowing them to learn from their experiences, adapt their strategies, and improve their performance over time. This continuous learning makes them more effective and efficient.
Memory and Context: Unlike the often stateless nature of chatbots, AI agents can maintain a persistent memory of past interactions, environmental states, and learned knowledge. This enables them to understand context, make more informed decisions, and engage in more meaningful, long-term interactions.
Integration with Systems: AI agents are often deeply integrated with various business systems, allowing them to access and process data from multiple sources, execute tasks within different applications, and orchestrate complex workflows.
In essence, while a chatbot is a tool for conversation, an AI agent is a tool for action and strategic execution. This fundamental difference opens up a vast array of possibilities for businesses seeking to automate more complex processes and gain deeper insights.
Diverse Applications of AI Agents Across Industries
Visualizing the Shift: AI Agents in Action
The versatility and advanced capabilities of AI agents mean they are not confined to a single industry or function. Their ability to automate complex workflows, analyze vast datasets, and make autonomous decisions makes them invaluable across a wide spectrum of business operations. Here are some key areas where AI agents are already making a significant impact or are poised to do so:
1. Customer Service and Experience
While chatbots handle basic inquiries, AI agents elevate customer service to a new level. They can:
Proactive Support: Monitor customer behavior and proactively offer assistance or relevant information before a customer even asks. For instance, an agent might detect a user struggling on a product page and offer a personalized tutorial or connect them with a human expert.
Personalized Interactions: Access and analyze a customer’s entire history, preferences, and past purchases to provide highly personalized recommendations and support, far beyond what a rule-based chatbot can achieve.
Complex Issue Resolution: Orchestrate solutions for multi-faceted customer problems by interacting with various internal systems (e.g., CRM, inventory, billing) to gather information, diagnose issues, and even initiate refunds or service changes autonomously.
Sentiment Analysis and Escalation: Continuously analyze customer sentiment during interactions and automatically escalate critical or negative experiences to human agents, providing them with a comprehensive summary of the situation.
2. Marketing and Sales
AI agents can revolutionize how businesses attract, engage, and convert customers:
Lead Qualification and Nurturing: Automatically identify high-potential leads from various sources, qualify them based on predefined criteria, and initiate personalized nurturing sequences through email, social media, or even direct outreach.
Dynamic Pricing and Promotions: Analyze real-time market data, competitor pricing, and customer demand to dynamically adjust product prices or offer personalized promotions to maximize revenue and conversion rates.
Content Personalization: Tailor website content, product recommendations, and marketing messages to individual users based on their browsing history, demographics, and inferred preferences, leading to higher engagement and conversion.
Campaign Optimization: Monitor the performance of marketing campaigns in real-time, identify underperforming elements, and autonomously make adjustments to targeting, bidding, or creative assets to improve ROI.
3. Operations and Supply Chain Management
In the realm of operations, AI agents can bring unprecedented efficiency and resilience:
Predictive Maintenance: Monitor equipment performance, analyze sensor data, and predict potential failures before they occur, scheduling maintenance proactively to minimize downtime and extend asset lifespan.
Inventory Optimization: Analyze sales forecasts, supply chain disruptions, and historical data to autonomously optimize inventory levels, reducing carrying costs while preventing stockouts.
Logistics and Route Optimization: Dynamically plan and adjust delivery routes, considering real-time traffic, weather conditions, and delivery priorities to ensure timely and cost-effective transportation.
Quality Control: Utilize computer vision and other sensors to inspect products on assembly lines, identify defects, and even initiate corrective actions or flag issues for human review.
4. Financial Services
AI agents are transforming finance through enhanced analysis and automation:
Fraud Detection: Continuously monitor transactions and behavioral patterns to detect and flag suspicious activities in real-time, significantly reducing financial losses due to fraud.
Algorithmic Trading: Execute trades based on complex algorithms and market analysis, reacting to market fluctuations faster than human traders.
Personalized Financial Advice: Analyze an individual’s financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance to provide tailored investment recommendations, budget planning, and debt management strategies.
Compliance and Risk Management: Automate the monitoring of regulatory changes, ensure adherence to compliance policies, and identify potential risks within financial operations.
5. Healthcare
In healthcare, AI agents hold the promise of improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency:
Diagnostic Assistance: Analyze patient data, medical images, and research papers to assist clinicians in diagnosing diseases more accurately and quickly.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Develop and adapt treatment plans based on a patient’s unique genetic makeup, medical history, and response to therapies.
Drug Discovery: Accelerate the drug discovery process by analyzing vast chemical libraries, predicting molecular interactions, and identifying potential drug candidates.
Patient Monitoring and Engagement: Remotely monitor patients’ vital signs, medication adherence, and recovery progress, proactively alerting healthcare providers to potential issues or engaging patients with personalized health information.
These examples merely scratch the surface of the potential applications of AI agents. As the technology matures and becomes more accessible, we can expect to see even more innovative and transformative uses emerge across every sector of the economy.
The Transformative Benefits of AI Agents for Businesses
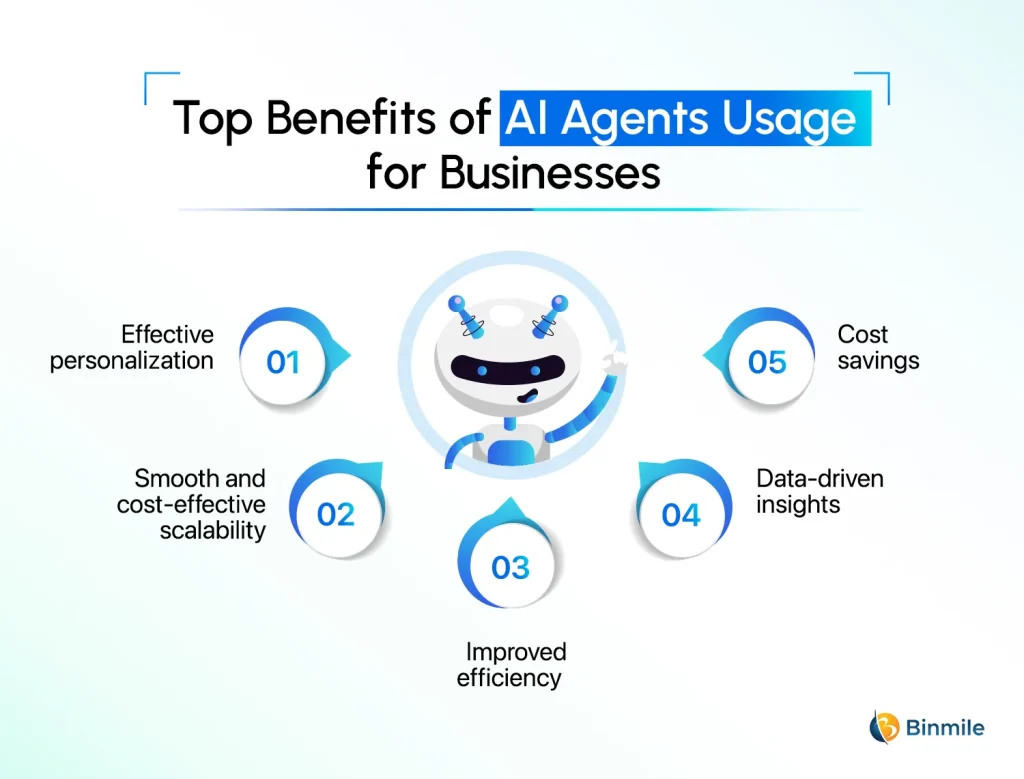
The adoption of AI agents is not merely a technological upgrade; it represents a strategic shift that can yield significant and multifaceted benefits for businesses. By moving beyond the reactive capabilities of chatbots to the proactive and autonomous nature of AI agents, organizations can unlock new levels of efficiency, intelligence, and competitive advantage.
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
One of the most immediate and tangible benefits of AI agents is the dramatic improvement in operational efficiency. By automating complex, multi-step tasks that previously required human intervention, AI agents free up valuable employee time. This allows human teams to focus on more strategic, creative, and high-value activities that require human ingenuity and emotional intelligence. For example, an AI agent can handle the entire process of lead qualification, data entry, and initial follow-up, allowing the sales team to concentrate on building relationships and closing deals. This automation extends beyond simple tasks; AI agents can orchestrate entire workflows, such as processing insurance claims or managing supply chain logistics, leading to faster turnaround times and reduced operational costs.
2. Improved Decision-Making and Strategic Insights
AI agents are not just doers; they are also thinkers. Their ability to access and analyze vast amounts of data from diverse sources—both internal and external—provides businesses with unprecedented insights. They can identify patterns, predict trends, and model potential outcomes that would be impossible for human analysts to uncover. For instance, an AI agent could analyze market trends, competitor activities, and customer sentiment to recommend a new product launch or a shift in marketing strategy. This data-driven decision-making reduces reliance on guesswork and intuition, leading to more effective strategies and better business outcomes. By providing real-time, actionable intelligence, AI agents empower leaders to make more informed and timely decisions.
3. Superior Customer Experience and Personalization
In today’s competitive landscape, customer experience is a key differentiator. AI agents enable businesses to deliver a level of personalization and proactive support that was previously unattainable at scale. By understanding each customer’s unique history, preferences, and behavior, AI agents can provide tailored recommendations, personalized content, and proactive assistance. Imagine an e-commerce AI agent that not only answers a customer’s question about a product but also suggests complementary items based on their past purchases and browsing history, and even proactively applies a personalized discount. This level of individualized attention fosters customer loyalty, increases customer lifetime value, and builds a stronger brand reputation.
4. Cost Reduction and Increased ROI
While there is an initial investment in implementing AI agent technology, the long-term return on investment can be substantial. Cost savings are realized through various channels: reduced labor costs from automating tasks, lower operational costs from improved efficiency, and minimized losses from proactive risk management (e.g., fraud detection, predictive maintenance). Furthermore, AI agents can directly contribute to revenue growth by optimizing pricing, improving sales conversion rates, and identifying new market opportunities. The ability of AI agents to operate 24/7 without fatigue or human error also contributes to a more consistent and reliable operation, further enhancing profitability.
5. Scalability and Agility
AI agents provide businesses with the ability to scale their operations and adapt to changing market conditions with greater agility. Unlike human teams, which require time for hiring and training, AI agents can be deployed and scaled almost instantly to meet fluctuating demand. This is particularly valuable for businesses with seasonal peaks or those experiencing rapid growth. Moreover, the learning capabilities of AI agents mean they can be retrained and repurposed to handle new tasks and challenges, providing a flexible and adaptable workforce that can evolve with the business. This agility allows organizations to respond more quickly to market shifts, competitive threats, and emerging opportunities, ensuring they remain resilient and competitive in a dynamic environment.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting AI Agents
While the benefits of AI agents are compelling, their successful adoption is not without challenges. Businesses embarking on this transformative journey must carefully consider several key factors to ensure a smooth transition and maximize their return on investment. Addressing these considerations proactively is crucial for mitigating risks and building a robust, ethical, and effective AI agent strategy.
1. Data Quality and Availability
AI agents, particularly those that learn and adapt, are only as good as the data they are trained on. Poor data quality—inaccurate, incomplete, inconsistent, or biased data—can lead to flawed decision-making, unreliable performance, and even perpetuate existing biases. Businesses must invest in robust data governance strategies, including data collection, cleaning, validation, and storage. Ensuring the availability of sufficient, high-quality, and relevant data is a foundational requirement for developing and deploying effective AI agents. This often involves integrating disparate data sources and establishing clear data pipelines.
2. Integration Complexity
AI agents often need to interact with a multitude of existing enterprise systems, databases, and applications to gather information and execute tasks. Integrating these complex systems can be a significant technical challenge. Legacy systems, disparate data formats, and a lack of standardized APIs can hinder seamless communication and data exchange. Businesses need to plan for robust integration architectures, potentially leveraging middleware, API management platforms, or microservices to ensure that AI agents can effectively access and orchestrate workflows across the entire technological ecosystem.
3. Ethical Implications and Bias
The autonomous nature of AI agents raises significant ethical concerns. If not carefully designed and monitored, AI agents can exhibit biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. For example, an AI agent used for loan approvals might inadvertently discriminate based on demographic data if the training data reflects historical biases. Businesses must prioritize ethical AI development, implementing fairness and transparency principles. This includes regular auditing of AI agent decisions, explainable AI (XAI) techniques to understand how decisions are made, and diverse development teams to identify and mitigate potential biases.
4. Security and Privacy
AI agents often handle sensitive customer and business data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Ensuring the security of AI systems and the privacy of the data they process is paramount. This involves implementing robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, access controls, and threat detection. Compliance with data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA is also critical. Businesses must establish clear policies for data handling, consent, and anonymization to protect sensitive information and maintain customer trust.
5. Human-AI Collaboration and Workforce Impact
The introduction of AI agents will inevitably change the nature of work. While AI agents can automate repetitive tasks, they are not intended to fully replace human employees but rather to augment their capabilities. Businesses need to focus on fostering effective human-AI collaboration, where AI agents handle routine tasks, allowing human employees to focus on complex problem-solving, creativity, and interpersonal interactions. This requires investing in reskilling and upskilling programs for the workforce, preparing them to work alongside AI agents and leverage their capabilities effectively. Managing employee expectations and addressing concerns about job displacement are also crucial for a successful transition.
6. Explainability and Trust
For businesses and users to trust AI agents, their decisions and actions must be explainable. The
concept of a ‘black box’ AI, where decisions are made without clear reasoning, can erode trust and make it difficult to diagnose errors or justify outcomes. Developing AI agents with built-in explainability features, such as providing justifications for their actions or highlighting the data points that influenced a decision, is essential. This transparency builds confidence among users, stakeholders, and regulators, facilitating broader adoption and ensuring accountability.
7. Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory environment surrounding AI is still nascent but rapidly evolving. Governments and international bodies are beginning to grapple with issues such as AI liability, data governance, and ethical guidelines. Businesses deploying AI agents must stay abreast of these developments and ensure their AI solutions comply with current and future regulations. Proactive engagement with legal and compliance experts is advisable to navigate this complex and changing landscape.
Conclusion: The Dawn of a New Era in Business Automation
The journey from simple chatbots to sophisticated AI agents marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of business automation and intelligence. We are moving beyond mere conversational interfaces to autonomous, proactive, and goal-oriented entities capable of orchestrating complex workflows, deriving deep insights from vast datasets, and making informed decisions. This shift promises a future where businesses can operate with unprecedented levels of efficiency, agility, and personalization.
AI agents are not just tools; they are strategic partners that can augment human capabilities, allowing employees to focus on creativity, innovation, and high-value interactions. From revolutionizing customer service and personalizing marketing efforts to optimizing supply chains and enhancing financial security, their applications are diverse and transformative. The benefits—including enhanced efficiency, improved decision-making, superior customer experience, significant cost reductions, and greater scalability—are compelling and offer a clear path to sustained competitive advantage.
However, the path to successful AI agent adoption requires careful navigation. Challenges related to data quality, integration complexity, ethical considerations, security, and workforce adaptation must be addressed with foresight and strategic planning. Businesses must prioritize responsible AI development, ensuring transparency, fairness, and robust data protection. Investing in employee training and fostering a culture of human-AI collaboration will be crucial for maximizing the potential of these powerful technologies.
As AI agents continue to mature and become more integrated into the fabric of business operations, they will undoubtedly reshape industries and redefine the competitive landscape. For organizations willing to embrace this new era of intelligent automation, the rewards will be substantial, paving the way for smarter growth, deeper insights, and a truly transformative future. The time to explore and invest in AI agents is now, not just to keep pace with the competition, but to lead the charge into the next frontier of business innovation.
Read More about AI with The Friends Fashions.





